Definition/Introduction :- Buchholz Relay is a device which is used to protect the transformer from all internal faults. It is gas actuated relay i.e. operates due to presence of gas produce in the main tank due to several internal faults. This relay took place between main tank and conservator at an angle of 7° to 15° (usually).
This relay used to protect transformer having Rating more than 500KVA, below this rating protection becomes uneconomical.
Working Principle of Buchholz Relay :-
Whenever, any internal fault occur inside the transformer, it heats the oil and the oil becomes evaporated. The evaporated gas which is low in weight lift up and passes through the buchholz relay and gas operate the murcury switch and gives command for further actions (e.g. tripping the transformer, maintenance work, fault detection ).
Construction of Buchholz Relay :-
It looks like a dome shaped vessel placed in the connecting pipe between the conservator and the main tank. The relays carries two fundamental parts or element which are nothing but murcury based switches. Upper element Consists of murcury switch with a hinged float. The Lower element consist of murcury switch which is Fixed on the hinged flap placed in the lower part and in the direction of flow of oil from Transformer main tank to conservator tank. The upper element closes the alarm circuit whether the lower element closes the trip coil and trip the transformer through circuit breaker in case of any internal fault. Elements are in different in mass, so that they could judge the level of fault automatically.
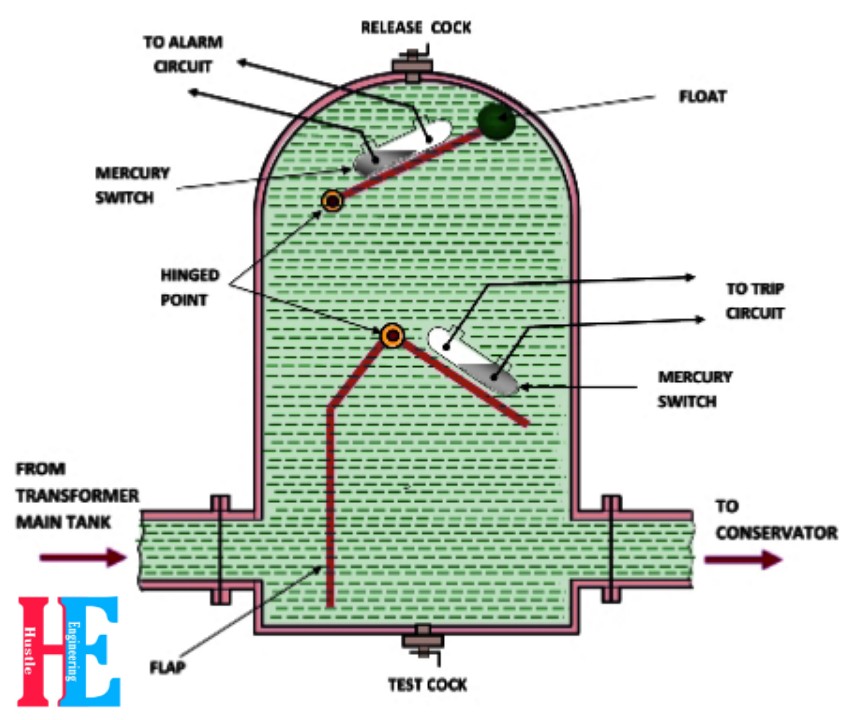
Operation :-
During any abnormal condition or at the time of fault occurs, there is a increase in temperature and the rate of increasing the temperature is directly proportional to the magnitude of fault.
So, whenever a minor fault occurs an arc produced and heat the oil present inside the main tank. Due to heating, oil decomposed. This decomposition contains more than 70% of hydrogen gas (Hydrogen gas is light in weight). This hydrogen gas lift upwards towards the conservator, but in middle there is buchholz relay and it traps the gas bubble in the upper part of the relay chamber. When a predetermined value of gas accumulated, it exerts a force on the float to tilt and close the contacts of the murcury switch which is attached with the hinged float. This process complete the alarm circuit and gives an alarm to the panel and the control room.
Whenever a major or serious fault occurs inside the transformer, high amount of gas generated inside the main tank. The oil of the tank rushes towards the Conservator through Buchholz relay. This process tilt the main flap of the relay and closes the contacts of the murcury switch. This completes trip circuit and gives command to the circuit breaker (CB) to trip or cut off the supply of the transformer.
*operating time of the relay is 0.1 second.
Release Cock :- As the name suggest it a simple valve which is used to release the pressure of the relay which were generated when fault took place.
Test Cock :- We need to check the properties of transformer oil ( e.g. insulation, moisture etc) after a predetermined interval of time. This is done to check whether the oil is capable or not to work efficiently. This test cock us used to take the oil from the transformer since there is no any way to get it in a perfect manner except this one. So that’s why we need a test cock.
Advantages :-
- This is the simplest form of Transformer protection
- It detects the incipient faults at a stage much earlier than other protection schemes.
Limitations :-
- The Buchholz Relay protection Scheme can only used in oil immersed Transformer.
- This relay can only detect the fault below the oil level.
- The response time of the relay is high.
